Real-time Tracking and Visualization
Tornado tracker – In the realm of tornado tracking, the advent of real-time monitoring systems has revolutionized our ability to anticipate and respond to these formidable weather events. These systems employ a diverse array of technologies, including radar, satellite imagery, and ground-based sensors, to provide a comprehensive view of tornado activity.
The relentless fury of tornadoes demands a keen eye, and tornado trackers stand as sentinels, their instruments piercing the heavens. One such tracker, the beryl live tracker , offers a lifeline to communities, providing real-time updates on the path of these destructive forces.
Armed with this knowledge, we can dance with the storm, knowing its every twist and turn, and ultimately emerge from its grasp, our lives intact.
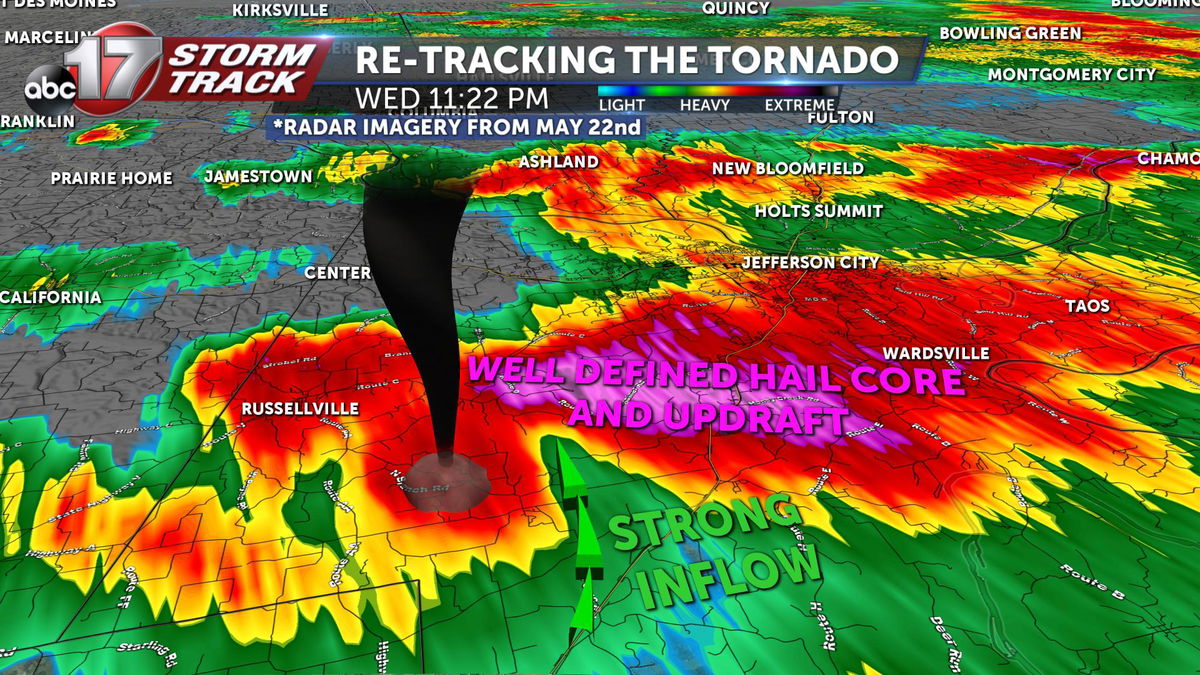
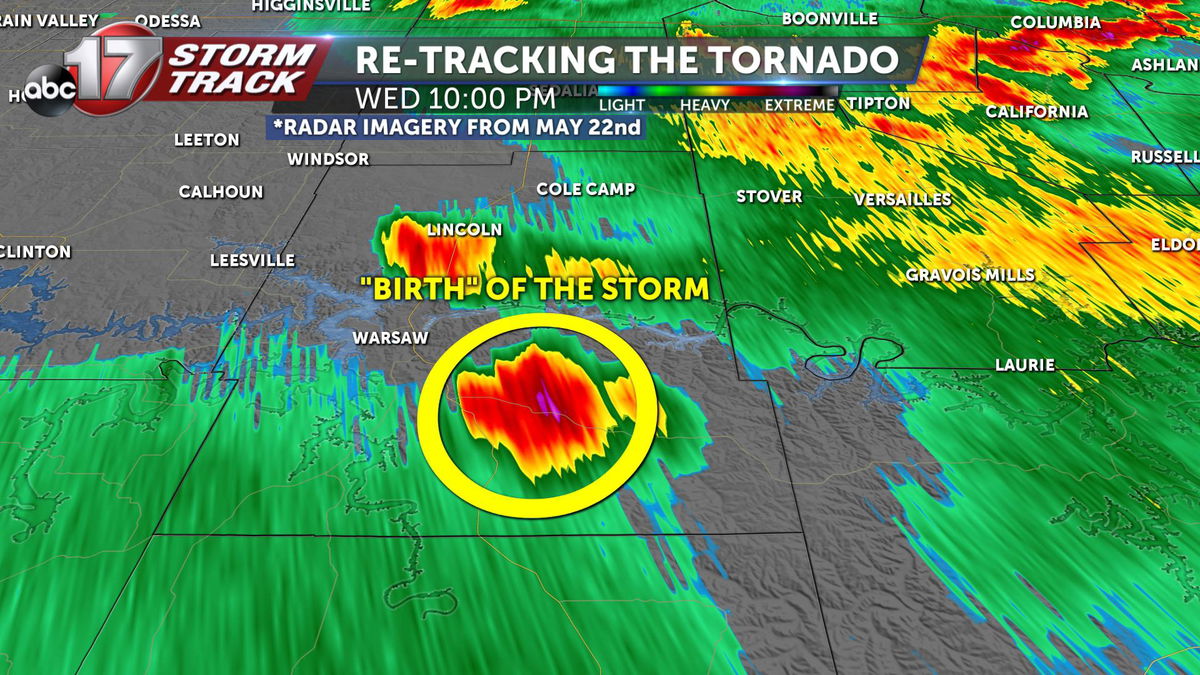
Radar technology plays a pivotal role in real-time tornado tracking. By transmitting radio waves into the atmosphere, radar systems can detect precipitation particles and determine their movement and intensity. This data is then processed to identify areas of rotation, which can indicate the presence of a tornado.
Interactive Maps and Dashboards
The proliferation of interactive maps and dashboards has made it possible for the public to access real-time tornado tracking information in a user-friendly format. These platforms provide a visual representation of tornado paths and intensity, allowing users to track the movement of these storms and make informed decisions about their safety.
Historical Tornado Data and Analysis: Tornado Tracker
Historical tornado data provides valuable insights into the patterns, trends, and risk associated with these severe weather events. Understanding this data is crucial for developing effective tornado warning systems, mitigation strategies, and emergency response plans.
Data Sources
Historical tornado data is primarily gathered from two main sources:
- Storm Reports: Collected by trained spotters and public reports, storm reports provide detailed information on tornado sightings, including location, time, and estimated intensity.
- Damage Surveys: Conducted by meteorologists and engineers, damage surveys assess the severity of tornado damage and assign a damage rating based on the Enhanced Fujita Scale (EF Scale).
Statistical Analysis
Statistical techniques are employed to analyze historical tornado data and identify patterns and trends. These techniques include:
- Frequency Analysis: Determines the average annual occurrence of tornadoes in a specific region.
- Distribution Analysis: Examines the geographical distribution of tornadoes, identifying areas with higher risk.
- Trend Analysis: Assesses changes in tornado frequency and intensity over time, providing insights into climate variability and long-term trends.
Key Historical Tornado Statistics, Tornado tracker
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Average Annual Occurrence (US) | 1,200-1,500 |
| Most Active Months (US) | April, May, June |
| Regions with Highest Risk (US) | Tornado Alley (Central US), Dixie Alley (Southeast US) |
Forecasting and Warning Systems
The ability to predict and provide timely warnings of tornadoes has significantly reduced the loss of life and property. Tornado forecasting and warning systems rely on a combination of numerical weather prediction models, storm spotter networks, and other technologies to detect and track tornadoes.
Numerical weather prediction models are computer programs that use mathematical equations to simulate the behavior of the atmosphere. These models can be used to predict the development of weather systems, including tornadoes, by analyzing data such as temperature, pressure, and wind speed. Storm spotter networks are composed of trained volunteers who report severe weather conditions, including tornadoes, to weather agencies. This information can be used to verify tornado warnings and to provide more accurate forecasts.
Types of Tornado Warnings
There are two main types of tornado warnings issued by weather agencies: tornado watches and tornado warnings.
- A tornado watch means that conditions are favorable for the development of tornadoes in a particular area. A tornado watch is typically issued when a severe thunderstorm warning has been issued and there is a risk of tornadoes developing.
- A tornado warning means that a tornado has been spotted or indicated by radar. A tornado warning is typically issued when a tornado is imminent or already occurring.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the advances in tornado forecasting and warning systems, there are still challenges and limitations in predicting and warning of tornadoes. One of the challenges is that tornadoes can develop very quickly, making it difficult to issue warnings in time. Additionally, tornadoes can be difficult to detect, especially in areas with low visibility or at night.
To improve warning accuracy, research is ongoing to develop new and improved forecasting models and to enhance the capabilities of storm spotter networks. Additionally, public education campaigns are important to raise awareness of tornado risks and to encourage people to take appropriate safety precautions.
Like the relentless dance of a tornado tracker, the path of Hurricane Beryl unfolds with equal precision. Track its every move with the hurricane beryl path tracker , a digital compass guiding you through the storm’s turbulent journey. From its genesis to its final dissipation, stay abreast of the tornado tracker’s insights, decoding the enigmatic language of the wind.